Dalvik虚拟机 - 类的加载
Dalvik虚拟机系列的文章力求将从虚拟机开始运行、类的加载/初始化、字节码的解释执行都覆盖到。加载类是我们最常接触但又不经常直接去显示加载的一个行为,本文从 ClassLoader.loadClass 说起来说明类加载的具体过程,这也将更容易理解主动修改类定义带来的一些如同hotpatch的功能。
1. APK被加载的流程
我们先来看用 ClassLoader 主动加载类的情况,我们都知道一个 APK 是被 DexClassLoader 加载起来的,第一个问题就是一个 APK 是在哪里被哪一个 DexClassLoader 加载的呢?
从《通过 startService 在新进程中启动服务的流程(一)》中我们知道,当要开启一个进程去承载新的应用程序时,会调用到 AMS 中的 startProcessLocked 函数,该函数最终又是通过调用 Process.start 方法请求 Zygote 进程 fork 目标进程的:
<center>
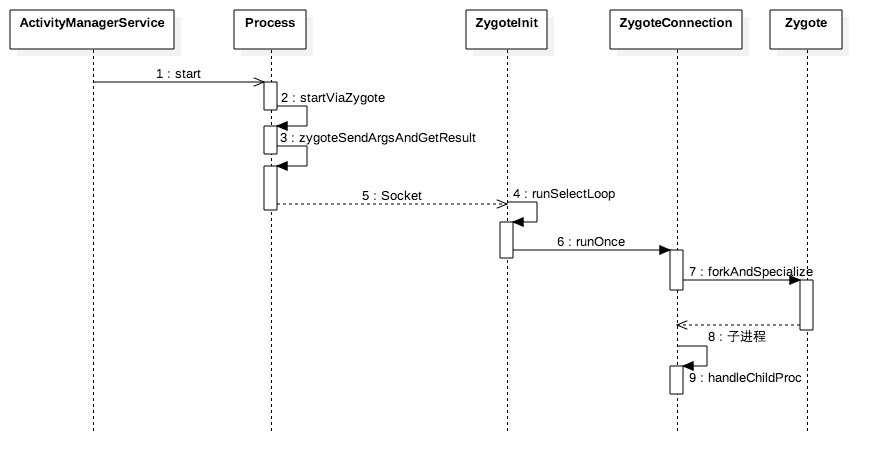
图1.1 从 Process.start() 到新进程创建(Android 4.4)</center>
图1.1展示了从 Process.start() 到新进程创建的过程,其中步骤7是fork新进程的过程,目标APK的加载就是在新进程创建后的步骤9中的,展开 handlerChildProc 函数:
private void handleChildProc(Arguments parsedArgs,
FileDescriptor[] descriptors, FileDescriptor pipeFd, PrintStream newStderr)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
......
if (parsedArgs.runtimeInit) {
......
} else {
String className;
try {
className = parsedArgs.remainingArgs[0];
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr,
"Missing required class name argument", null);
return;
}
String[] mainArgs = new String[parsedArgs.remainingArgs.length - 1];
System.arraycopy(parsedArgs.remainingArgs, 1,
mainArgs, 0, mainArgs.length);
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
WrapperInit.execStandalone(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
parsedArgs.classpath, className, mainArgs);
} else {
ClassLoader cloader;
if (parsedArgs.classpath != null) {
* cloader = new PathClassLoader(parsedArgs.classpath,
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
} else {
cloader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
}
try {
ZygoteInit.invokeStaticMain(cloader, className, mainArgs);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Error starting.", ex);
}
}
}
}
从上面代码中带*的一行可以看出,加载 APK 中所有类的 ClassLoader 是 PathClassLoader,它和 DexClassLoader 一样,基类均是 BaseDexClassLoader.
2. 加载类
2.1 基本流程
在 APK 的 ClassLoader 被指定后,APK 包中所有类(不包括代码中动态加载的dex包)都由该 ClassLoader 来加载,我们从 PathClassLoader 的 loadClass 方法看起,由于 PathClassLoader 并没有复写 loadClass,所以调用的仍是 ClassLoader 类的 loadClass 方法:
<center>
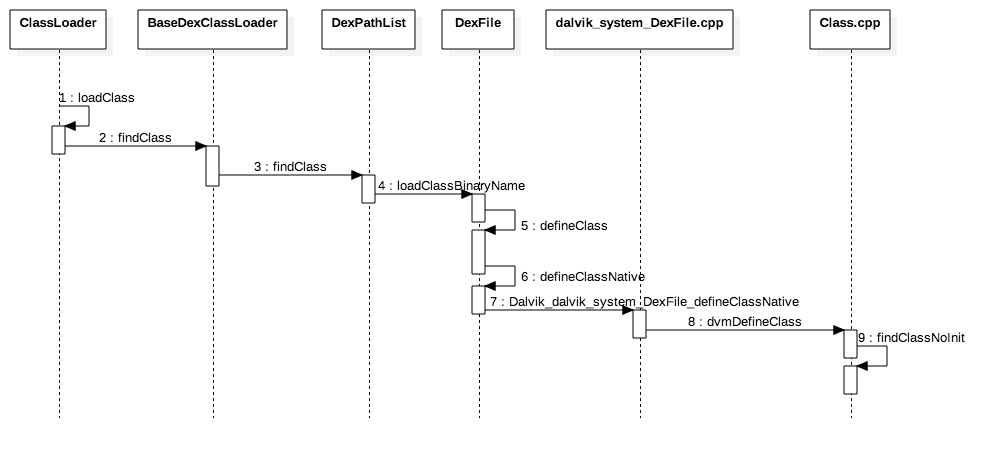
图2.1 loadClass 流程</center>
图2.1展示了加载一个类的基本流程,可以发现在 android 中废除了 java 基础类 ClassLoader 中的 defineClass 方法,改为调用 DexFile 的 defineClass 方法,然后到了 native 层执行 Class.cpp 中的 findClassNoInit 方法,在findClassNoInit 中执行寻找类、加载类的逻辑,但不会执行初始化类的逻辑,findClassNoInit 的定义为:
ClassObject* findClassNoInit(const char* descriptor, Object* loader, DvmDex* pDvmDex);从 findClassNoInit 的定义中看出,第三个参数类型是 DvmDex,它就是加载进来的 Dex 文件,它是在图2.1第7步Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_defineClassNative 函数传过来的:
static void Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_defineClassNative(const u4* args,
JValue* pResult)
{
......
if (pDexOrJar->isDex)
pDvmDex = dvmGetRawDexFileDex(pDexOrJar->pRawDexFile);
......
}不过它并不是在这创建的,因为 dvmGetRawDexFileDex 函数只是取出本来就存在 pDexOrJar->pRawDexFile 结构体里的 DvmDex 对象,下一小节我们就来看Dex文件是如何加载的。
2.2 Dex文件的加载
我们先来看一下 DvmDex 结构体:
struct DvmDex {
/* pointer to the DexFile we're associated with */
DexFile* pDexFile; // 关联的DexFile指针
/* clone of pDexFile->pHeader (it's used frequently enough) */
const DexHeader* pHeader; // pDexFile->pHeader的复制
/* interned strings; parallel to "stringIds" */
struct StringObject** pResStrings; //
/* resolved classes; parallel to "typeIds" */
struct ClassObject** pResClasses; // 解析过的类
/* resolved methods; parallel to "methodIds" */
struct Method** pResMethods; // 解析过的方法
/* resolved instance fields; parallel to "fieldIds" */
/* (this holds both InstField and StaticField) */
struct Field** pResFields; // 解析过的字段,既包括实例字段也包括静态字段
/* interface method lookup cache */
struct AtomicCache* pInterfaceCache; //
/* shared memory region with file contents */
bool isMappedReadOnly;
MemMapping memMap;
jobject dex_object;
/* lock ensuring mutual exclusion during updates */
pthread_mutex_t modLock;
};实际上DvmDex是在ClassLoader构造时创建的,ClassLoader 其实就是指 PathClassLoader 了。
<center>
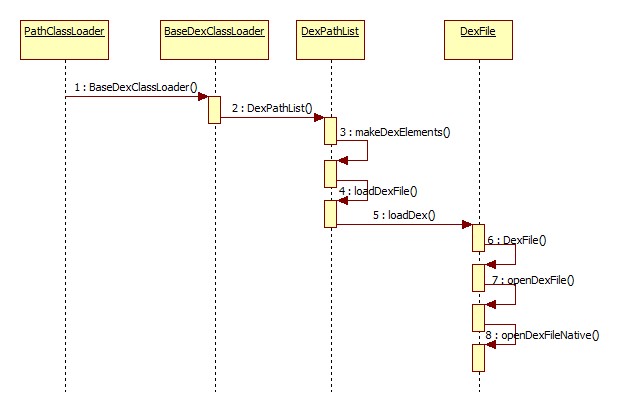
图2.2 ClassLoader 创建过程中 Dex 文件的加载流程</center>
图2.2展示了 PathClassLoader 创建的基本过程(java层)中 Dex 文件的加载流程,代码调用就不再赘述了,openDexFileNative 是个 native 函数,代码是在 dalvik/vm/native/dalvik_system_DexFile.cpp,函数名 Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_openDexFileNative():
static void Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_openDexFileNative(const u4* args,
JValue* pResult)
{
......
/*
* Try to open it directly as a DEX if the name ends with ".dex".
* If that fails (or isn't tried in the first place), try it as a
* Zip with a "classes.dex" inside.
*/
if (hasDexExtension(sourceName)
1. && dvmRawDexFileOpen(sourceName, outputName, &pRawDexFile, false) == 0) {
ALOGV("Opening DEX file '%s' (DEX)", sourceName);
pDexOrJar = (DexOrJar*) malloc(sizeof(DexOrJar));
pDexOrJar->isDex = true;
pDexOrJar->pRawDexFile = pRawDexFile;
pDexOrJar->pDexMemory = NULL;
} else if (dvmJarFileOpen(sourceName, outputName, &pJarFile, false) == 0) {
......
} else {
......
}
if (pDexOrJar != NULL) {
pDexOrJar->fileName = sourceName;
2. addToDexFileTable(pDexOrJar);
} else {
free(sourceName);
}
free(outputName);
RETURN_PTR(pDexOrJar);
}步骤1:打开 dex 文件并进行优化与加载 (dvmRawDexFileOpen)(至于 jar 包或者 apk 的加载其实就是比 dex 文件的加载多一步解压);
步骤2:将创建的 DexOrJar 对象加入“用户加载过的 dex 文件”的哈希表中 (addToDexFileTable)。
我们这里只看 dvmRawDexFileOpen 函数:
int dvmRawDexFileOpen(const char* fileName, const char* odexOutputName,
RawDexFile** ppRawDexFile, bool isBootstrap) // odexOutputName 就是 odex 文件的所在地
{
......
1. dexFd = open(fileName, O_RDONLY);
......
if (odexOutputName == NULL) {
cachedName = dexOptGenerateCacheFileName(fileName, NULL);
if (cachedName == NULL)
goto bail;
} else {
2. cachedName = strdup(odexOutputName);
}
ALOGV("dvmRawDexFileOpen: Checking cache for %s (%s)",
fileName, cachedName);
3. optFd = dvmOpenCachedDexFile(fileName, cachedName, modTime,
adler32, isBootstrap, &newFile, /*createIfMissing=*/true);
if (optFd < 0) {
ALOGI("Unable to open or create cache for %s (%s)",
fileName, cachedName);
goto bail;
}
locked = true;
/*
* If optFd points to a new file (because there was no cached
* version, or the cached version was stale), generate the
* optimized DEX. The file descriptor returned is still locked,
* and is positioned just past the optimization header.
*/
if (newFile) {
u8 startWhen, copyWhen, endWhen;
bool result;
off_t dexOffset;
dexOffset = lseek(optFd, 0, SEEK_CUR);
result = (dexOffset > 0);
if (result) {
startWhen = dvmGetRelativeTimeUsec();
4. result = copyFileToFile(optFd, dexFd, fileSize) == 0;
copyWhen = dvmGetRelativeTimeUsec();
}
if (result) {
5. result = dvmOptimizeDexFile(optFd, dexOffset, fileSize,
fileName, modTime, adler32, isBootstrap);
}
if (!result) {
ALOGE("Unable to extract+optimize DEX from '%s'", fileName);
goto bail;
}
endWhen = dvmGetRelativeTimeUsec();
ALOGD("DEX prep '%s': copy in %dms, rewrite %dms",
fileName,
(int) (copyWhen - startWhen) / 1000,
(int) (endWhen - copyWhen) / 1000);
}
/*
* Map the cached version. This immediately rewinds the fd, so it
* doesn't have to be seeked anywhere in particular.
*/
6. if (dvmDexFileOpenFromFd(optFd, &pDvmDex) != 0) {
ALOGI("Unable to map cached %s", fileName);
goto bail;
}
if (locked) {
/* unlock the fd */
if (!dvmUnlockCachedDexFile(optFd)) {
/* uh oh -- this process needs to exit or we'll wedge the system */
ALOGE("Unable to unlock DEX file");
goto bail;
}
locked = false;
}
ALOGV("Successfully opened '%s'", fileName);
*ppRawDexFile = (RawDexFile*) calloc(1, sizeof(RawDexFile));
(*ppRawDexFile)->cacheFileName = cachedName;
7. (*ppRawDexFile)->pDvmDex = pDvmDex;
cachedName = NULL; // don't free it below
result = 0;
bail:
free(cachedName);
if (dexFd >= 0) {
close(dexFd);
}
if (optFd >= 0) {
if (locked)
(void) dvmUnlockCachedDexFile(optFd);
close(optFd);
}
return result;
}步骤1:打开 dex 文件,文件句柄是 dexFd;
步骤2:cacheName 就是 odexOutputName,也就是 odex(optimized DEX,即优化过的 dex) 文件的所在路径;
步骤3:打开 odex 文件,如果没有就创建它,如果是要创建新的,就填充头信息进去,如果是既有的,那就验证头信息;
步骤4:拷贝 dex 文件的所有内容到 odex 文件中,当然是在头信息后面;
步骤5:优化 dex 文件,简单来讲就是执行命令行程序 /bin/dexopt,其中重要的一步是将 Dex 文件中的类信息数组做一个映射哈希表,优化过的文件内容仍保存在 odex 中;
步骤6:把 odex 的内容映射到 pDvmDex 中,实际上是映射到了 DexFile 结构体,DvmDex 包含了 DexFile,和已经解析了的类、方法、字段信息,在这里就不再细细展开映射过程了,说一下 DexFile 的映射结构:
<center>
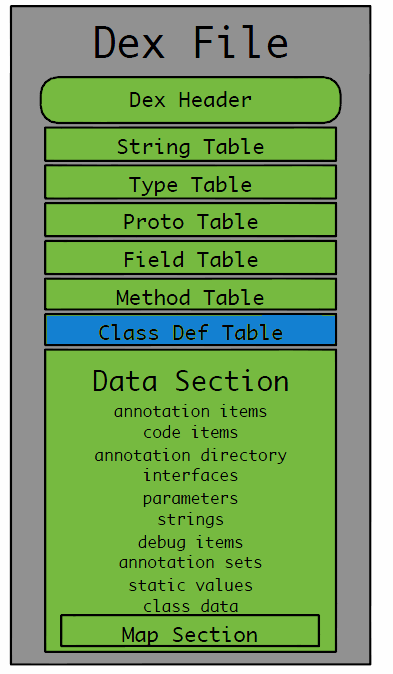
图2.3 DexFile 映射结构</center>
如图2.3所示(这是我直接盗的图啦啦啦),从 Dex Header 往下,依次会有 String、Type、Proto、Field、Method、Class Def 六个表,对应到 DexFile 结构体中:
/*
* Structure representing a DEX file.
*
* Code should regard DexFile as opaque, using the API calls provided here
* to access specific structures.
*/
struct DexFile {
/* directly-mapped "opt" header */
const DexOptHeader* pOptHeader;
/* pointers to directly-mapped structs and arrays in base DEX */
const DexHeader* pHeader;
const DexStringId* pStringIds;
const DexTypeId* pTypeIds;
const DexFieldId* pFieldIds;
const DexMethodId* pMethodIds;
const DexProtoId* pProtoIds;
const DexClassDef* pClassDefs;
......
};可以看出,这六个表实际上就是映射成一个个的结构体数组了,下文提到的一些 idx 结尾的一些变量,以及类加载的 CLASS_IDX 状态,都是与这些结构体数组的下标挂钩的。
步骤7:将 pDvmDex 赋值到 RawDexFile 结构体中。
简单用图说明下 DvmDex、DexFile、RawDexFile 之间的包含关系:
<center>
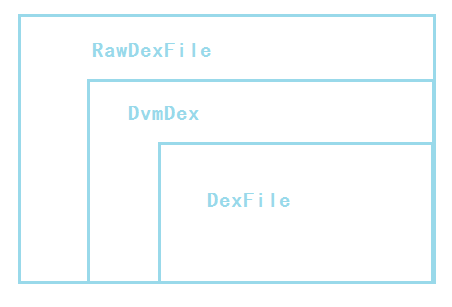
图2.4 DvmDex、DexFile、RawDexFile 之间的包含关系</center>
回过头来,看函数 Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_openDexFileNative 的步骤1,发现 dvmRawDexFileOpen 的作用就是给 DexOrJar 的成员 RawDexFile* pRawDexFile 赋值,赋值后返回这个 DexOrJar,在 java 层对应的就是一个 int 值 DexFile.mCookie,对应图2.2中的步骤6(DexFile的构造函数):
public DexFile(String fileName) throws IOException {
mCookie = openDexFile(fileName, null, 0);
mFileName = fileName;
guard.open("close");
//System.out.println("DEX FILE cookie is " + mCookie);
}2.3 findClassNoInit
2.2节我们分析了 DvmDex 和 DexOrJar,这一节回到 findClassNoInit 函数:
<center>
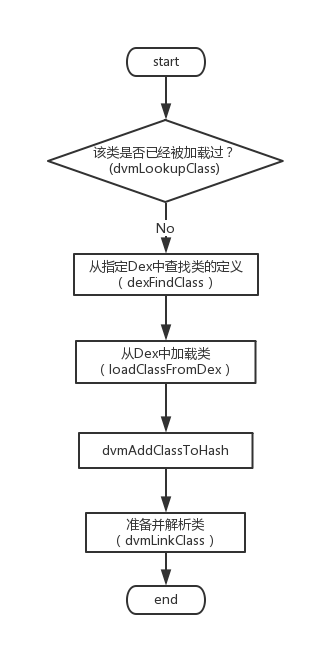
图2.5 findClassNoInit 流程</center>
如图2.3所示为 findClassNoInit 的流程,关键代码如下,其中步骤1-步骤5分别对应上面流程图的5部分:
static ClassObject* findClassNoInit(const char* descriptor, Object* loader,
DvmDex* pDvmDex)
{
Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf();
ClassObject* clazz;
......
1. clazz = dvmLookupClass(descriptor, loader, true);
if (clazz == NULL) {
const DexClassDef* pClassDef;
......
if (pDvmDex == NULL) {
assert(loader == NULL); /* shouldn't be here otherwise */
pDvmDex = searchBootPathForClass(descriptor, &pClassDef);
} else {
2. pClassDef = dexFindClass(pDvmDex->pDexFile, descriptor);
}
......
/* found a match, try to load it */
3. clazz = loadClassFromDex(pDvmDex, pClassDef, loader);
if (dvmCheckException(self)) {
/* class was found but had issues */
if (clazz != NULL) {
dvmFreeClassInnards(clazz);
dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc((Object*) clazz, NULL);
}
goto bail;
}
/*
* Lock the class while we link it so other threads must wait for us
* to finish. Set the "initThreadId" so we can identify recursive
* invocation. (Note all accesses to initThreadId here are
* guarded by the class object's lock.)
*/
dvmLockObject(self, (Object*) clazz);
clazz->initThreadId = self->threadId;
/*
* Add to hash table so lookups succeed.
*
* [Are circular references possible when linking a class?]
*/
assert(clazz->classLoader == loader);
4. if (!dvmAddClassToHash(clazz)) {
/*
* Another thread must have loaded the class after we
* started but before we finished. Discard what we've
* done and leave some hints for the GC.
*
* (Yes, this happens.)
*/
//ALOGW("WOW: somebody loaded %s simultaneously", descriptor);
clazz->initThreadId = 0;
dvmUnlockObject(self, (Object*) clazz);
/* Let the GC free the class.
*/
dvmFreeClassInnards(clazz);
dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc((Object*) clazz, NULL);
/* Grab the winning class.
*/
clazz = dvmLookupClass(descriptor, loader, true);
assert(clazz != NULL);
goto got_class;
}
dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc((Object*) clazz, NULL);
#if LOG_CLASS_LOADING
logClassLoadWithTime('>', clazz, startTime);
#endif
/*
* Prepare and resolve.
*/
5. if (!dvmLinkClass(clazz)) {
......
}
dvmObjectNotifyAll(self, (Object*) clazz);
dvmUnlockObject(self, (Object*) clazz);
/*
* Add class stats to global counters.
*
* TODO: these should probably be atomic ops.
*/
gDvm.numLoadedClasses++;
gDvm.numDeclaredMethods +=
clazz->virtualMethodCount + clazz->directMethodCount;
gDvm.numDeclaredInstFields += clazz->ifieldCount;
gDvm.numDeclaredStaticFields += clazz->sfieldCount;
/*
* Cache pointers to basic classes. We want to use these in
* various places, and it's easiest to initialize them on first
* use rather than trying to force them to initialize (startup
* ordering makes it weird).
*/
if (gDvm.classJavaLangObject == NULL &&
strcmp(descriptor, "Ljava/lang/Object;") == 0)
{
/* It should be impossible to get here with anything
* but the bootclasspath loader.
*/
assert(loader == NULL);
gDvm.classJavaLangObject = clazz;
}
#if LOG_CLASS_LOADING
logClassLoad('<', clazz);
#endif
} else {
got_class:
......
}
......
return clazz;
}2.3.1 dvmLookupClass
首先查找指定类加载器加载过的类,如果已经加载,则不会执行加载的逻辑。其实在 loadClass 函数中,第一步也是查找该类是否已经被该类加载器加载过(findLoadedClass),它实际也是和这里一样调用 dvmLookupClass:
ClassObject* dvmLookupClass(const char* descriptor, Object* loader,
bool unprepOkay)
{
ClassMatchCriteria crit;
void* found;
u4 hash;
crit.descriptor = descriptor;
crit.loader = loader;
......
1. found = dvmHashTableLookup(gDvm.loadedClasses, hash, &crit,
hashcmpClassByCrit, false);
......
2. if (found && !unprepOkay && !dvmIsClassLinked((ClassObject*)found)) {
ALOGV("Ignoring not-yet-ready %s, using slow path",
((ClassObject*)found)->descriptor);
found = NULL;
}
return (ClassObject*) found;
}步骤1:从已经加载过的类(gDvm.loadedClasses)哈希表中查找该类是否存在(存在哈希表中并不表示加载了),key的类型是ClassMatchCriteria,该结构体定义如下:
struct ClassMatchCriteria {
const char* descriptor;
Object* loader;
};从 ClassMatchCriteria 的结构可以看出,类描述和加载器完全一样才算是匹配。
步骤2:如果找到匹配了,判断该类是否已经链接,如果已经链接,就是已经被加载了,如果还没有链接,那就仍被认为没找到:
INLINE bool dvmIsClassLinked(const ClassObject* clazz) {
return clazz->status >= CLASS_RESOLVED;
}dvmIsClassLinked 是个内联函数,它其实就是判断类的状态是否是已经解析(CLASS_RESOLVED),ClassObject 的 status 字段其实有 8 种状态(CLASS_ERROR 除外):
enum ClassStatus {
CLASS_ERROR = -1,
CLASS_NOTREADY = 0,
CLASS_IDX = 1, /* loaded, DEX idx in super or ifaces */
CLASS_LOADED = 2, /* DEX idx values resolved */
CLASS_RESOLVED = 3, /* part of linking */
CLASS_VERIFYING = 4, /* in the process of being verified */
CLASS_VERIFIED = 5, /* logically part of linking; done pre-init */
CLASS_INITIALIZING = 6, /* class init in progress */
CLASS_INITIALIZED = 7, /* ready to go */
};在后面的篇幅里会一一说明每个类型是在什么情况下赋值的。
2.3.2 dexFindClass
如果通过 dvmLookupClass 发现该类没有加载,就会首先通过dexFindClass从加载进来的 Dex 文件中查找该类的定义,该函数是在 DexFile.cpp 中:
const DexClassDef* dexFindClass(const DexFile* pDexFile,
const char* descriptor)
{
const DexClassLookup* pLookup = pDexFile->pClassLookup;
u4 hash;
int idx, mask;
hash = classDescriptorHash(descriptor);
mask = pLookup->numEntries - 1;
1. idx = hash & mask;
/*
* Search until we find a matching entry or an empty slot.
*/
while (true) {
int offset;
offset = pLookup->table[idx].classDescriptorOffset;
2. if (offset == 0)
return NULL;
if (pLookup->table[idx].classDescriptorHash == hash) {
const char* str;
str = (const char*) (pDexFile->baseAddr + offset);
if (strcmp(str, descriptor) == 0) {
3. return (const DexClassDef*)
(pDexFile->baseAddr + pLookup->table[idx].classDefOffset);
}
}
idx = (idx + 1) & mask;
}
}步骤1:DexFile::pClassLookup 实际上是在加载 Dex 文件时解析的每个类存储的一个映射表,key 是通过类的说明descriptor计算的哈希,value 是存放解析的类的偏移吗,这一步是计算hash和表的下标;
步骤2:如果找到最后都没找到,就返回NULL;
步骤3:找到了就返回该类定义 DexClassDef:
struct DexClassDef {
u4 classIdx; /* index into typeIds for this class */
u4 accessFlags;
u4 superclassIdx; /* index into typeIds for superclass */
u4 interfacesOff; /* file offset to DexTypeList */
u4 sourceFileIdx; /* index into stringIds for source file name */
u4 annotationsOff; /* file offset to annotations_directory_item */
u4 classDataOff; /* file offset to class_data_item */
u4 staticValuesOff; /* file offset to DexEncodedArray */
};2.3.3 loadClassFromDex
static ClassObject* loadClassFromDex(DvmDex* pDvmDex,
const DexClassDef* pClassDef, Object* classLoader)
{
ClassObject* result;
DexClassDataHeader header;
const u1* pEncodedData;
const DexFile* pDexFile;
assert((pDvmDex != NULL) && (pClassDef != NULL));
pDexFile = pDvmDex->pDexFile;
if (gDvm.verboseClass) {
ALOGV("CLASS: loading '%s'...",
dexGetClassDescriptor(pDexFile, pClassDef));
}
1. pEncodedData = dexGetClassData(pDexFile, pClassDef);
if (pEncodedData != NULL) {
2. dexReadClassDataHeader(&pEncodedData, &header);
} else {
// Provide an all-zeroes header for the rest of the loading.
memset(&header, 0, sizeof(header));
}
3. result = loadClassFromDex0(pDvmDex, pClassDef, &header, pEncodedData,
classLoader);
if (gDvm.verboseClass && (result != NULL)) {
ALOGI("[Loaded %s from DEX %p (cl=%p)]",
result->descriptor, pDvmDex, classLoader);
}
return result;
}步骤1:拿到 ClassData 的指针;
步骤2:读取 ClassData 的头信息
步骤3:根据前两步拿到的信息loadClass:
static ClassObject* loadClassFromDex0(DvmDex* pDvmDex,
const DexClassDef* pClassDef, const DexClassDataHeader* pHeader,
const u1* pEncodedData, Object* classLoader)
{
ClassObject* newClass = NULL;
......
/*
* Allocate storage for the class object on the GC heap, so that other
* objects can have references to it. We bypass the usual mechanism
* (allocObject), because we don't have all the bits and pieces yet.
*
* Note that we assume that java.lang.Class does not override
* finalize().
*/
/* TODO: Can there be fewer special checks in the usual path? */
assert(descriptor != NULL);
if (classLoader == NULL &&
strcmp(descriptor, "Ljava/lang/Class;") == 0) {
assert(gDvm.classJavaLangClass != NULL);
newClass = gDvm.classJavaLangClass;
} else {
size_t size = classObjectSize(pHeader->staticFieldsSize);
1. newClass = (ClassObject*) dvmMalloc(size, ALLOC_NON_MOVING);
}
if (newClass == NULL)
return NULL;
2. DVM_OBJECT_INIT(newClass, gDvm.classJavaLangClass); // 初始化 java.lang.Class 成员
dvmSetClassSerialNumber(newClass); // 初始化 serialNumber
newClass->descriptor = descriptor; // 类全描述
assert(newClass->descriptorAlloc == NULL);
SET_CLASS_FLAG(newClass, pClassDef->accessFlags); // 类访问权限
3. dvmSetFieldObject((Object *)newClass,
OFFSETOF_MEMBER(ClassObject, classLoader),
(Object *)classLoader); // 初始化 ClassLoader
newClass->pDvmDex = pDvmDex;
newClass->primitiveType = PRIM_NOT;
newClass->status = CLASS_IDX; // 初始化类加载状态为 CLASS_IDX
/*
* Stuff the superclass index into the object pointer field. The linker
* pulls it out and replaces it with a resolved ClassObject pointer.
* I'm doing it this way (rather than having a dedicated superclassIdx
* field) to save a few bytes of overhead per class.
*
* newClass->super is not traversed or freed by dvmFreeClassInnards, so
* this is safe.
*/
assert(sizeof(u4) == sizeof(ClassObject*)); /* 32-bit check */
4. newClass->super = (ClassObject*) pClassDef->superclassIdx;
/*
* Stuff class reference indices into the pointer fields.
*
* The elements of newClass->interfaces are not traversed or freed by
* dvmFreeClassInnards, so this is GC-safe.
*/
const DexTypeList* pInterfacesList;
5. pInterfacesList = dexGetInterfacesList(pDexFile, pClassDef);
if (pInterfacesList != NULL) {
newClass->interfaceCount = pInterfacesList->size;
newClass->interfaces = (ClassObject**) dvmLinearAlloc(classLoader,
newClass->interfaceCount * sizeof(ClassObject*));
for (i = 0; i < newClass->interfaceCount; i++) {
const DexTypeItem* pType = dexGetTypeItem(pInterfacesList, i);
newClass->interfaces[i] = (ClassObject*)(u4) pType->typeIdx;
}
dvmLinearReadOnly(classLoader, newClass->interfaces);
}
/* load field definitions */
/*
* Over-allocate the class object and append static field info
* onto the end. It's fixed-size and known at alloc time. This
* seems to increase zygote sharing. Heap compaction will have to
* be careful if it ever tries to move ClassObject instances,
* because we pass Field pointers around internally. But at least
* now these Field pointers are in the object heap.
*/
6. if (pHeader->staticFieldsSize != 0) {
/* static fields stay on system heap; field data isn't "write once" */
int count = (int) pHeader->staticFieldsSize;
u4 lastIndex = 0;
DexField field;
newClass->sfieldCount = count;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
dexReadClassDataField(&pEncodedData, &field, &lastIndex);
loadSFieldFromDex(newClass, &field, &newClass->sfields[i]);
}
}
7. if (pHeader->instanceFieldsSize != 0) {
int count = (int) pHeader->instanceFieldsSize;
u4 lastIndex = 0;
DexField field;
newClass->ifieldCount = count;
newClass->ifields = (InstField*) dvmLinearAlloc(classLoader,
count * sizeof(InstField));
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
dexReadClassDataField(&pEncodedData, &field, &lastIndex);
loadIFieldFromDex(newClass, &field, &newClass->ifields[i]);
}
dvmLinearReadOnly(classLoader, newClass->ifields);
}
/*
* Load method definitions. We do this in two batches, direct then
* virtual.
*
* If register maps have already been generated for this class, and
* precise GC is enabled, we pull out pointers to them. We know that
* they were streamed to the DEX file in the same order in which the
* methods appear.
*
* If the class wasn't pre-verified, the maps will be generated when
* the class is verified during class initialization.
*/
u4 classDefIdx = dexGetIndexForClassDef(pDexFile, pClassDef);
const void* classMapData;
u4 numMethods;
if (gDvm.preciseGc) {
classMapData =
dvmRegisterMapGetClassData(pDexFile, classDefIdx, &numMethods);
/* sanity check */
if (classMapData != NULL &&
pHeader->directMethodsSize + pHeader->virtualMethodsSize != numMethods)
{
ALOGE("ERROR: in %s, direct=%d virtual=%d, maps have %d",
newClass->descriptor, pHeader->directMethodsSize,
pHeader->virtualMethodsSize, numMethods);
assert(false);
classMapData = NULL; /* abandon */
}
} else {
classMapData = NULL;
}
8. if (pHeader->directMethodsSize != 0) {
int count = (int) pHeader->directMethodsSize;
u4 lastIndex = 0;
DexMethod method;
newClass->directMethodCount = count;
newClass->directMethods = (Method*) dvmLinearAlloc(classLoader,
count * sizeof(Method));
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
dexReadClassDataMethod(&pEncodedData, &method, &lastIndex);
loadMethodFromDex(newClass, &method, &newClass->directMethods[i]);
if (classMapData != NULL) {
const RegisterMap* pMap = dvmRegisterMapGetNext(&classMapData);
if (dvmRegisterMapGetFormat(pMap) != kRegMapFormatNone) {
newClass->directMethods[i].registerMap = pMap;
/* TODO: add rigorous checks */
assert((newClass->directMethods[i].registersSize+7) / 8 ==
newClass->directMethods[i].registerMap->regWidth);
}
}
}
dvmLinearReadOnly(classLoader, newClass->directMethods);
}
9. if (pHeader->virtualMethodsSize != 0) {
int count = (int) pHeader->virtualMethodsSize;
u4 lastIndex = 0;
DexMethod method;
newClass->virtualMethodCount = count;
newClass->virtualMethods = (Method*) dvmLinearAlloc(classLoader,
count * sizeof(Method));
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
dexReadClassDataMethod(&pEncodedData, &method, &lastIndex);
loadMethodFromDex(newClass, &method, &newClass->virtualMethods[i]);
if (classMapData != NULL) {
const RegisterMap* pMap = dvmRegisterMapGetNext(&classMapData);
if (dvmRegisterMapGetFormat(pMap) != kRegMapFormatNone) {
newClass->virtualMethods[i].registerMap = pMap;
/* TODO: add rigorous checks */
assert((newClass->virtualMethods[i].registersSize+7) / 8 ==
newClass->virtualMethods[i].registerMap->regWidth);
}
}
}
dvmLinearReadOnly(classLoader, newClass->virtualMethods);
}
newClass->sourceFile = dexGetSourceFile(pDexFile, pClassDef);
/* caller must call dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc */
return newClass;
}第一步:分配 ClassObject 对象(newClass)的内存;
第二步:初始化该类的 java.lang.Class 成员,每一个 java 对象在 native 层都会对应的 ClassObject 结构体其实都是继承于 Object:
struct Object {
/* ptr to class object */
ClassObject* clazz;
/*
* A word containing either a "thin" lock or a "fat" monitor. See
* the comments in Sync.c for a description of its layout.
*/
u4 lock;
};
struct ClassObject : Object {
...
};即每一种对象都会有8字节的头。这一步就是初始化这个 clazz 成员;
第三步:初始化 ClassLoader、Dex对象、加载状态等,此时的状态为 CLASS_IDX,区别于 CLASS_LOADED,CLASS_IDX 状态时 ClassObject 中的成员都不是直接的指针/引用而是数字下标index;
第四步:父类(newClass->super)初始化;
第五步:接口(newClass->interfaces)初始化;
第六步:静态成员初始化;
第七步:实例成员初始化;
第八步:普通函数初始化;
第九步:虚函数初始化;
2.3.4 dvmAddClassToHash
这一步就是将加载了的类添加进哈希表 gDvm.loadedClasses 中:
bool dvmAddClassToHash(ClassObject* clazz)
{
......
* found = dvmHashTableLookup(gDvm.loadedClasses, hash, clazz,
hashcmpClassByClass, true);
......
return (found == (void*) clazz);
}dvmHashTableLookup 的最后一个参数代表是否在没有查找到的时候添加进去,具体我看就不必展开了。
2.3.5 dvmLinkClass
前面讲的 loadClassFromDex 是将 ClassObject 中接口、方法信息以索引(index)的形式存起来了(说句题外话,大家可以看下在 DexFile.h 中定义的这几个结构体,classIdx、protoIdx 的类型均是 u2,即两个字节,这是不是就意味着类、方法的总数都是最多2^16-1个呢???),本节讲的 dvmLinkClass 则会将这些索引替换为真正的引用:
bool dvmLinkClass(ClassObject* clazz)
{
......
/* "Resolve" the class.
*
* At this point, clazz's reference fields may contain Dex file
* indices instead of direct object references. Proxy objects are
* an exception, and may be the only exception. We need to
* translate those indices into real references, and let the GC
* look inside this ClassObject.
*/
if (clazz->status == CLASS_IDX) {
......
superclassIdx = (u4) clazz->super;
clazz->super = NULL;
/* After this line, clazz will be fair game for the GC. The
* superclass and interfaces are all NULL.
*/
clazz->status = CLASS_LOADED;
if (superclassIdx != kDexNoIndex) {
1. ClassObject* super = dvmResolveClass(clazz, superclassIdx, false);
if (super == NULL) {
assert(dvmCheckException(dvmThreadSelf()));
if (gDvm.optimizing) {
/* happens with "external" libs */
ALOGV("Unable to resolve superclass of %s (%d)",
clazz->descriptor, superclassIdx);
} else {
ALOGW("Unable to resolve superclass of %s (%d)",
clazz->descriptor, superclassIdx);
}
goto bail;
}
dvmSetFieldObject((Object *)clazz,
OFFSETOF_MEMBER(ClassObject, super),
(Object *)super);
}
2. if (clazz->interfaceCount > 0) {
/* Resolve the interfaces implemented directly by this class. */
assert(interfaceIdxArray != NULL);
dvmLinearReadWrite(clazz->classLoader, clazz->interfaces);
for (i = 0; i < clazz->interfaceCount; i++) {
assert(interfaceIdxArray[i] != kDexNoIndex);
clazz->interfaces[i] =
dvmResolveClass(clazz, interfaceIdxArray[i], false);
......
}
dvmLinearReadOnly(clazz->classLoader, clazz->interfaces);
}
}
/*
* There are now Class references visible to the GC in super and
* interfaces.
*/
/*
* All classes have a direct superclass, except for
* java/lang/Object and primitive classes. Primitive classes are
* are created CLASS_INITIALIZED, so won't get here.
*/
assert(clazz->primitiveType == PRIM_NOT);
if (strcmp(clazz->descriptor, "Ljava/lang/Object;") == 0) {
......
} else {
if (clazz->super == NULL) {
dvmThrowLinkageError("no superclass defined");
goto bail;
}
/* verify */
3. if (dvmIsFinalClass(clazz->super)) {
ALOGW("Superclass of '%s' is final '%s'",
clazz->descriptor, clazz->super->descriptor);
dvmThrowIncompatibleClassChangeError("superclass is final");
goto bail;
} else if (dvmIsInterfaceClass(clazz->super)) {
ALOGW("Superclass of '%s' is interface '%s'",
clazz->descriptor, clazz->super->descriptor);
dvmThrowIncompatibleClassChangeError("superclass is an interface");
goto bail;
} else if (!dvmCheckClassAccess(clazz, clazz->super)) {
ALOGW("Superclass of '%s' (%s) is not accessible",
clazz->descriptor, clazz->super->descriptor);
dvmThrowIllegalAccessError("superclass not accessible");
goto bail;
}
/* Inherit finalizability from the superclass. If this
* class also overrides finalize(), its CLASS_ISFINALIZABLE
* bit will already be set.
*/
if (IS_CLASS_FLAG_SET(clazz->super, CLASS_ISFINALIZABLE)) {
SET_CLASS_FLAG(clazz, CLASS_ISFINALIZABLE);
}
/* See if this class descends from java.lang.Reference
* and set the class flags appropriately.
*/
4. if (IS_CLASS_FLAG_SET(clazz->super, CLASS_ISREFERENCE)) {
u4 superRefFlags;
/* We've already determined the reference type of this
* inheritance chain. Inherit reference-ness from the superclass.
*/
superRefFlags = GET_CLASS_FLAG_GROUP(clazz->super,
CLASS_ISREFERENCE |
CLASS_ISWEAKREFERENCE |
CLASS_ISFINALIZERREFERENCE |
CLASS_ISPHANTOMREFERENCE);
SET_CLASS_FLAG(clazz, superRefFlags);
} else if (clazz->classLoader == NULL &&
clazz->super->classLoader == NULL &&
strcmp(clazz->super->descriptor,
"Ljava/lang/ref/Reference;") == 0)
{
u4 refFlags;
/* This class extends Reference, which means it should
* be one of the magic Soft/Weak/PhantomReference classes.
*/
refFlags = CLASS_ISREFERENCE;
if (strcmp(clazz->descriptor,
"Ljava/lang/ref/SoftReference;") == 0)
{
/* Only CLASS_ISREFERENCE is set for soft references.
*/
} else if (strcmp(clazz->descriptor,
"Ljava/lang/ref/WeakReference;") == 0)
{
refFlags |= CLASS_ISWEAKREFERENCE;
} else if (strcmp(clazz->descriptor,
"Ljava/lang/ref/FinalizerReference;") == 0)
{
refFlags |= CLASS_ISFINALIZERREFERENCE;
} else if (strcmp(clazz->descriptor,
"Ljava/lang/ref/PhantomReference;") == 0)
{
refFlags |= CLASS_ISPHANTOMREFERENCE;
} else {
/* No-one else is allowed to inherit directly
* from Reference.
*/
//xxx is this the right exception? better than an assertion.
dvmThrowLinkageError("illegal inheritance from Reference");
goto bail;
}
/* The class should not have any reference bits set yet.
*/
assert(GET_CLASS_FLAG_GROUP(clazz,
CLASS_ISREFERENCE |
CLASS_ISWEAKREFERENCE |
CLASS_ISFINALIZERREFERENCE |
CLASS_ISPHANTOMREFERENCE) == 0);
SET_CLASS_FLAG(clazz, refFlags);
}
}
/*
* Populate vtable.
*/
5. if (dvmIsInterfaceClass(clazz)) {
/* no vtable; just set the method indices */
int count = clazz->virtualMethodCount;
if (count != (u2) count) {
ALOGE("Too many methods (%d) in interface '%s'", count,
clazz->descriptor);
goto bail;
}
dvmLinearReadWrite(clazz->classLoader, clazz->virtualMethods);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
clazz->virtualMethods[i].methodIndex = (u2) i;
dvmLinearReadOnly(clazz->classLoader, clazz->virtualMethods);
} else {
if (!createVtable(clazz)) {
ALOGW("failed creating vtable");
goto bail;
}
}
/*
* Populate interface method tables. Can alter the vtable.
*/
6. if (!createIftable(clazz))
goto bail;
/*
* Insert special-purpose "stub" method implementations.
*/
7. if (!insertMethodStubs(clazz))
goto bail;
/*
* Compute instance field offsets and, hence, the size of the object.
*/
8. if (!computeFieldOffsets(clazz))
goto bail;
/*
* Cache field and method info for the class Reference (as loaded
* by the boot classloader). This has to happen after the call to
* computeFieldOffsets().
*/
if ((clazz->classLoader == NULL)
&& (strcmp(clazz->descriptor, "Ljava/lang/ref/Reference;") == 0)) {
if (!precacheReferenceOffsets(clazz)) {
ALOGE("failed pre-caching Reference offsets");
dvmThrowInternalError(NULL);
goto bail;
}
}
/*
* Compact the offsets the GC has to examine into a bitmap, if
* possible. (This has to happen after Reference.referent is
* massaged in precacheReferenceOffsets.)
*/
computeRefOffsets(clazz);
/*
* Done!
*/
9. if (IS_CLASS_FLAG_SET(clazz, CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED))
clazz->status = CLASS_VERIFIED;
else
clazz->status = CLASS_RESOLVED;
okay = true;
if (gDvm.verboseClass)
ALOGV("CLASS: linked '%s'", clazz->descriptor);
/*
* We send CLASS_PREPARE events to the debugger from here. The
* definition of "preparation" is creating the static fields for a
* class and initializing them to the standard default values, but not
* executing any code (that comes later, during "initialization").
*
* We did the static prep in loadSFieldFromDex() while loading the class.
*
* The class has been prepared and resolved but possibly not yet verified
* at this point.
*/
if (gDvm.debuggerActive) {
dvmDbgPostClassPrepare(clazz);
}
bail:
if (!okay) {
clazz->status = CLASS_ERROR;
if (!dvmCheckException(dvmThreadSelf())) {
dvmThrowVirtualMachineError(NULL);
}
}
if (interfaceIdxArray != NULL) {
free(interfaceIdxArray);
}
return okay;
}第一步:替换 clazz->super(父类)为真的父类 ClassObject 引用,这里用到了 dvmResolveClass 方法,本文虽然是从 ClassLoader.loadClass 说起的,但其实最常见的就是在解释器在执行某方法时,遇到某类没有解析过,就会执行 dvmResolveClass 方法去解析:
ClassObject* dvmResolveClass(const ClassObject* referrer, u4 classIdx,
bool fromUnverifiedConstant)
{
......
1. resClass = dvmDexGetResolvedClass(pDvmDex, classIdx); //
if (resClass != NULL)
return resClass;
......
if (className[0] != '\0' && className[1] == '\0') {
/* primitive type */
resClass = dvmFindPrimitiveClass(className[0]);
} else {
2. resClass = dvmFindClassNoInit(className, referrer->classLoader);
}
if (resClass != NULL) {
......
3. dvmDexSetResolvedClass(pDvmDex, classIdx, resClass);
} else {
......
}
return resClass;
}(1) 查找已经解析了的类(已经解析了的类状态是 CLASS_RESOLVED)
(2) 若该类没有解析,则执行 dvmFindClassNoInit 加载类并解析,这个 dvmFindClassNoInit 是干嘛的呢?看起来跟前面说的 findClassNoInit 差不多,其实它最终就是反调java层的 ClassLoader.loadClass 去加载类,这时候是不是又回到了文章开头了 ~·~
(3) 将该类加入已解析类的表中
第二步:interfaceIdxArray 是事先已经复copy赋值为 clazz->interfaces 的,这步是给 clazz->interfaces 重新赋值为接口的引用,接口也是 ClassObject;
第三步:如果该类不是 java.lang.Object 的话,那么就必须有父类,判断父类是否是 final 的、是否是个接口、是否有访问权限
第四步:SoftReference、WeakReference 一类的类特殊对待;
第五步:对于非接口类,vtable 的创建;
第六步:接口表 iftable 的创建
第七步:虚函数的实现全部换为native实现 - 抛一个 “abstract method not implemented” 的 AbstractMethodError;
第八步:调整(将引用调至非引用之前,所有双宽度字段都已经对齐)并计算字段偏移,以及类的大小;
第九步:基本结束了,如果该类在 dexopt 阶段预先通过了 dvmVerifyClass,打上了 CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED 标记,则该类的状态标识为 CLASS_VERIFIED,否则标识为 CLASS_RESOLVED。
2.4 小结
至此,类加载的过程就算完成了,java 中执行的代码肯定是方法体,即解释器解释执行的过程就是方法执行的过程,这时候也会伴随类的初始化<cinit>以及对象初始化<init>,下一节将会讲解类的初始化相关的内容。